how much sodium is in turkey
/turkey_annotated-b66cb3d317d44f35be63a0e5b1117f5b.jpg) Turkey Nutrition Facts and Health Benefits
Turkey Nutrition Facts and Health BenefitsNutritionEverything you need to know about Turkey Carne Turkey is a great native bird of North America. He is hunted in nature, as well as raised in farms. Its meat is highly nutritious and a popular protein source consumed worldwide. This article tells you everything you need to know about turkey, including your nutrition, calories, and how to add it to your diet. Turkey is nutrient-rich. Two thick slices (84 grams) of turkey contain ():Turkey nutrients depend on cutting. For example, dark meat, which is found in active muscles such as legs or thighs, tends to have more fat and calories than white meat, while white meat contains (, ).In addition, turkey skin is high in fat. This means that skin cuts have more calories and fat than skin-free cuts. For example, 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of turkey with skin packs 169 calories and 5.5 grams of fat, while the same amount without the skin has 139 calories and only 2 grams of fat (). Note that the calorie difference is small. In addition, fat can after meals (). Summary Turkey is rich in proteins and an excellent source of many vitamins and minerals, especially vitamins B. Skin-free cuts have less calories and less fat than skin-free cuts. Turkey is rich in proteins and an excellent source of many vitamins and minerals, especially vitamins B. Skin-free cuts have less calories and less fat than skin-free cuts. Turkey has several potential health benefits. Healthy Source of ProteinTurkey is a .Protein is important for muscle growth and maintenance. It gives structure to the cells and helps to transport nutrients around your body (, ).In addition, a high protein diet can even support weight loss by promoting feelings of fullness (, ).Only 2 thick slices (84 grams) of turkey pack 24 grams of protein, an impressive 48% of DV (). In addition, turkey may be a healthier alternative to red meat, as some observational studies link red meat with a higher risk of colon cancer and heart disease (, , ).However, other studies claim that — not red meat itself — has a negative effect on health (, , ). Charge with BTurkey vitamins is a particularly rich source of Bcina vitamins, including B3 (B3). Two thick slices (84 grams) of turkey pack 61% of DV for , 49% for vitamin B6, and 29% for vitamin B12 (). These have many benefits: In addition, turkey is a good source of folate and B1 (thiamine) and B2 (riboflavin) (). Rubber FountainThe turkey is loaded with selenium, zinc and phosphorus. helps your body produce thyroid hormones, which regulate your metabolism and growth rate (, ). Zinc is an essential mineral necessary for many different body processes, such as gene expression, protein synthesis and enzyme reactions (, ).Finally, phosphorus is vital for (). In addition, turkey provides small amounts of magnesium and potassium. Summary Turkey is a great source of high quality protein, as well as many B vitamins and several minerals. Turkey is a great source of high quality protein, as well as many B vitamins and several minerals. Although this meat has many benefits, it is important to limit processed turkey products, as these items can be. Processed varieties, such as turkey ham, sausages and nuggets, can accommodate large amounts of salt. Sodium is usually added as a condom or flavor enhancer (). Research shows that consuming excess salt can increase the risk of stomach cancer. Conversely, cutting salt intake can reduce high blood pressure (, ).Some processed turkey products such as salami and pastrami maintain up to 75% of the DV for sodium by 3.5 ounces (100 grams). The same portion of turkey sausages provides more than 60% of the DV (, , ).In comparison, 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of unprocessed turkey, cooked provides only 31% of the DV for sodium (). Therefore, to minimize salt intake, choose the unprocessed turkey on processed forms. Summary The processed turkey products often pack excessive amounts of salt. To avoid excess consumption, choose the turkey without processing. Processed turkey products often pack excessive amounts of salt. To avoid excess consumption, choose the turkey without processing. You can include turkey in your diet in infinite ways. The fresh or frozen turkey can be purchased all year from your local grocery store or butcher shop. This meat is often roasted in the oven, but it can also be taken slowly using a slow coconut or a coconut pot until tender. It can be added to the following dishes: Turkey can also be bought chopped and used to replace beef in dishes such as Bolognese spaghetti or home cake. As indicated above, it is better to limit your consumption of processed turkey products such as sausages and sandwich meat. Summary Turkey is incredibly versatile and can be added to soups, salads and casseroles. It also makes a big replacement for beef. Turkey is incredibly versatile and can be added to soups, salads and pots. It also makes a big replacement for beef. Turkey is a popular meat that has high quality proteins, vitamins B, selenium, and phosphorus. It can support various aspects of health, including muscle growth and maintenance, due to its abundant supply of nutrients. However, it is better to avoid processed varieties, as they are high in salt. You can easily include this meat in soups, curries and many other dishes. Read this now.
/turkey-crop-74909f3624504149b970586e921239af.jpg)
Low Sodium Lunch Meat: Brands and Tips

Sliced turkey Nutrition Facts - Eat This Much

Turkey: Nutrition, Calories, Benefits, and More
/turkey-bacon_annotated-08ea061a00a743478e73f67e047264eb.jpg)
Turkey Bacon Nutrition Facts and Health Benefits
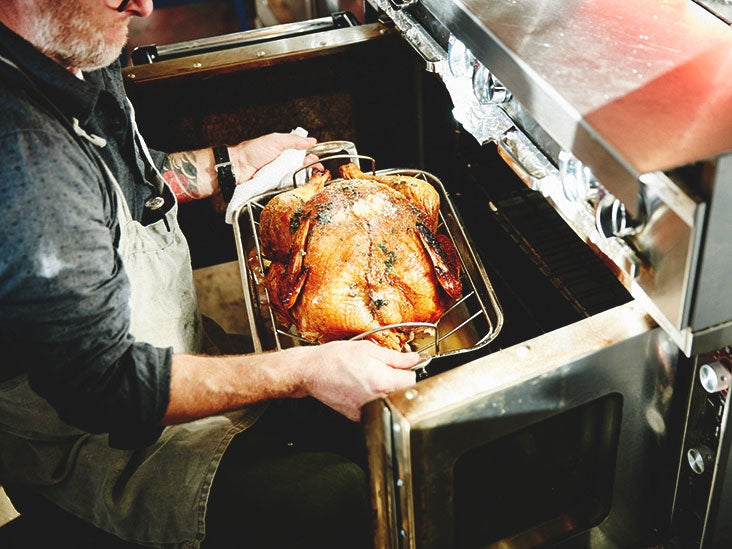

Turkey: Nutrition, Calories, Benefits, and More

How to Brine a Turkey & How to Salt a Turkey

Products - Deli Meat - Natural Honey & Maple Turkey Breast - Applegate

46% Lower Sodium Turkey Breast | Boar's Head

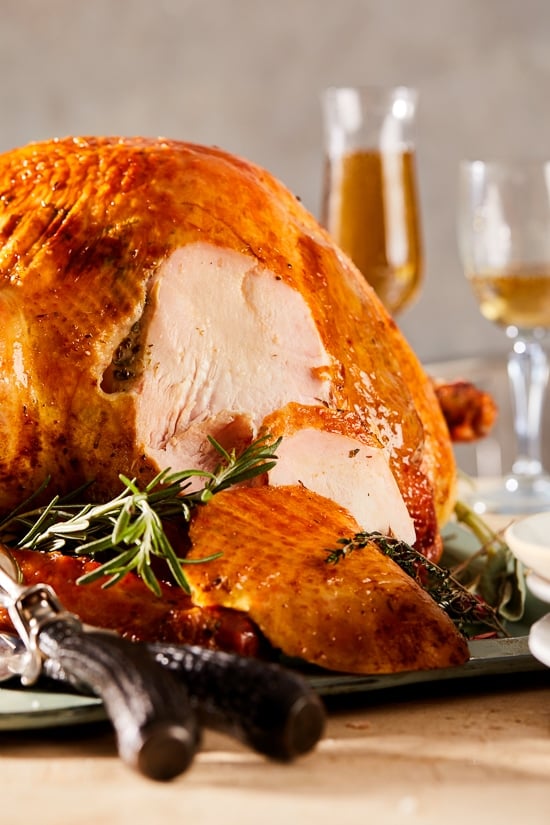
Salt and Pepper Turkey Recipe | Martha Stewart

Salt and Pepper Turkey Recipe | Martha Stewart

Turkey: Nutrition, benefits, and diet

Nutrition: Let's talk turkey — and sodium | Duluth News Tribune
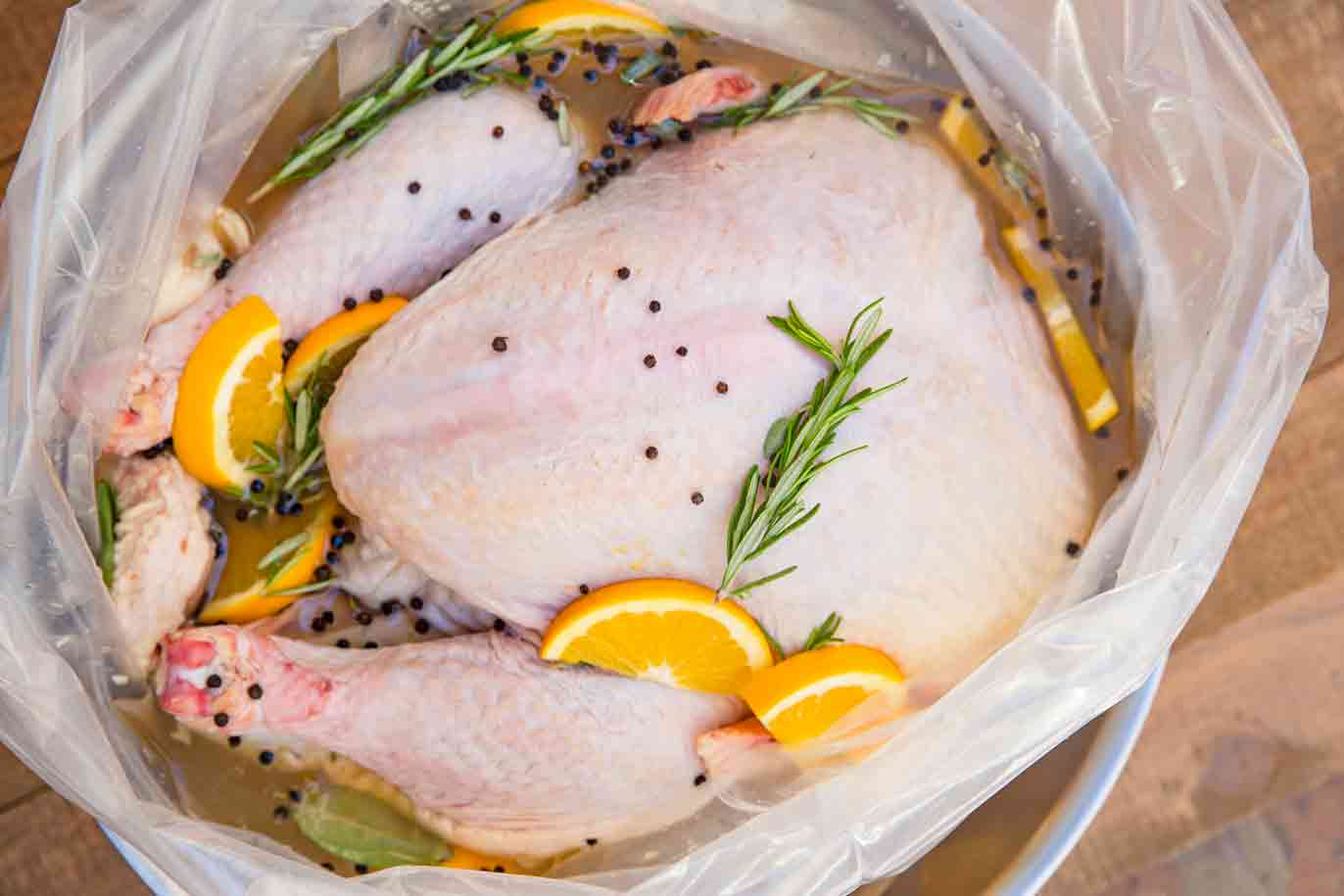

Turkey Brine - Dinner, then Dessert
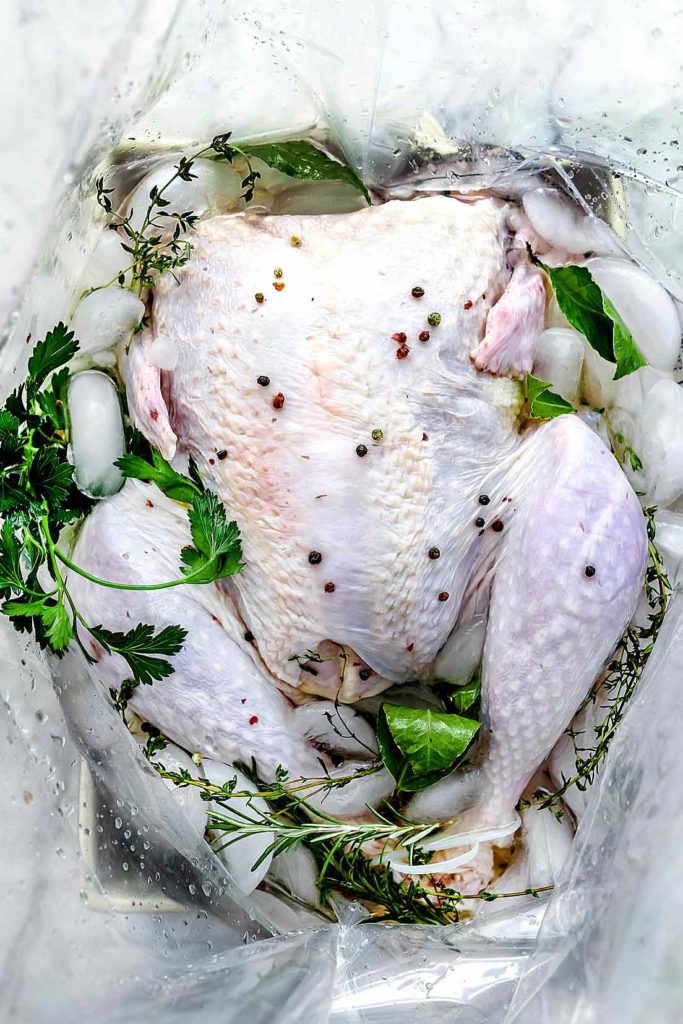

Turkey Brine 101 (The BEST Wet and Dry Brines) | foodiecrush.com
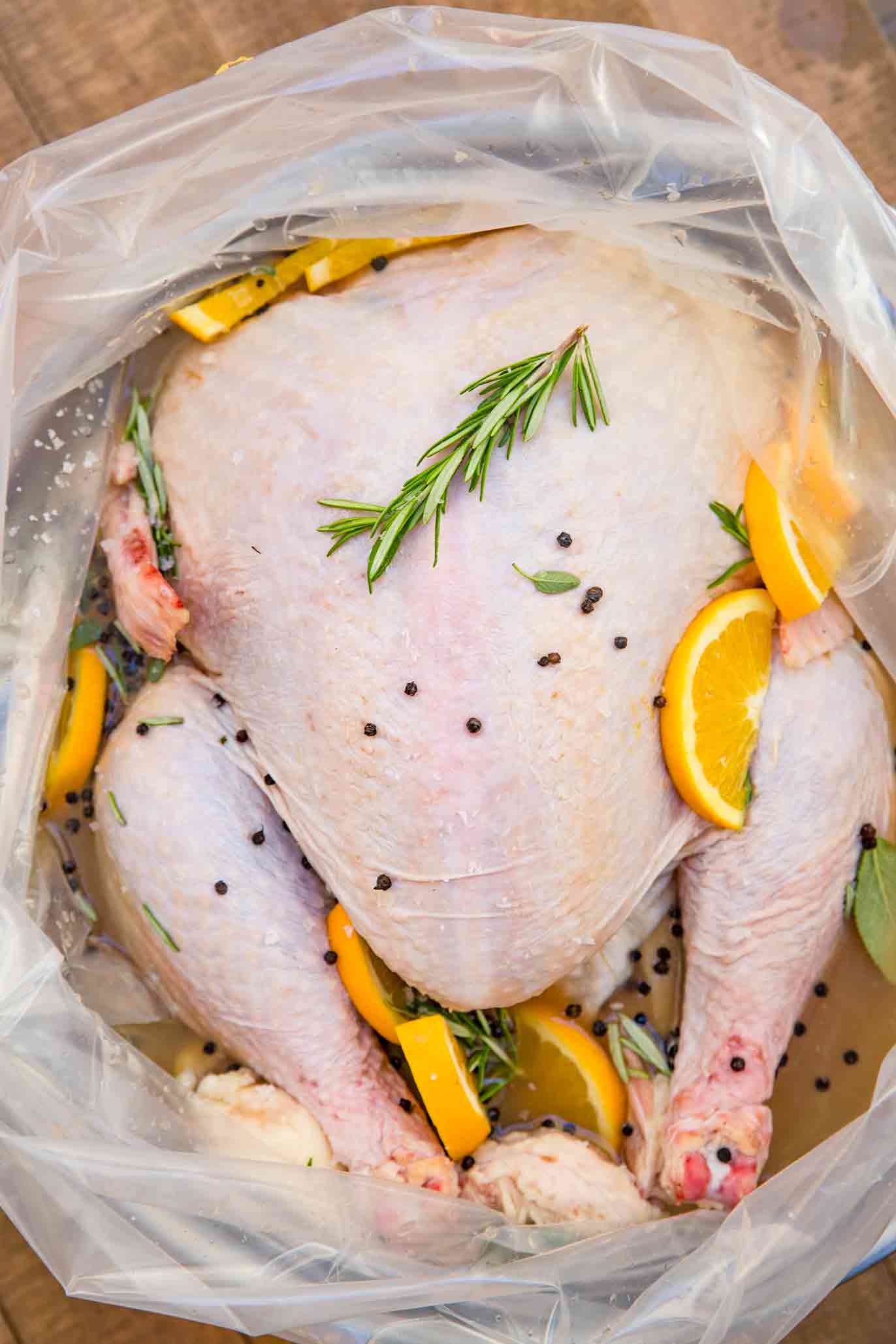

Turkey Brine - Dinner, then Dessert
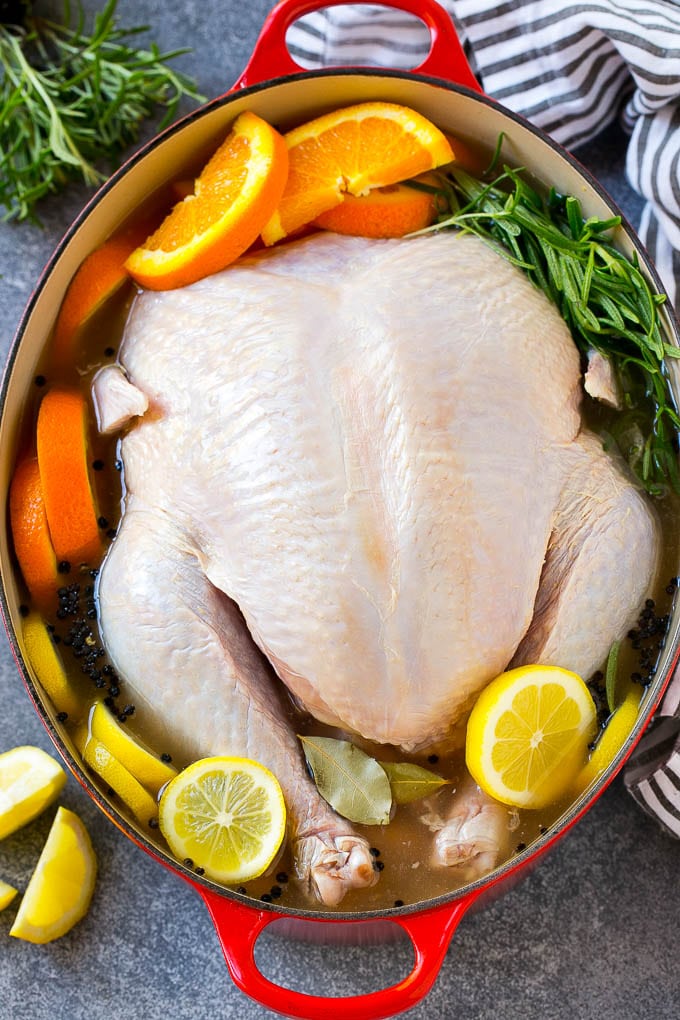

Turkey Brine Recipe - Dinner at the Zoo
/bacon_annotated2-1efa80033a7f4f9ebb9fb187773aafe7.jpg)
Bacon Nutrition Facts: Calories, Carbs, and Health Info

Herb and Salt-Rubbed Dry Brine Turkey - Skinnytaste

Low-Sodium Deli Turkey (Page 1) - Line.17QQ.com

Is Turkey Bacon Healthy? Nutrition, Calories and More

Why Brining Keeps Turkey and Other Meat So Moist - How-To - FineCooking

Dry Brine Turkey - How To Dry Brine A Turkey | Kitchn
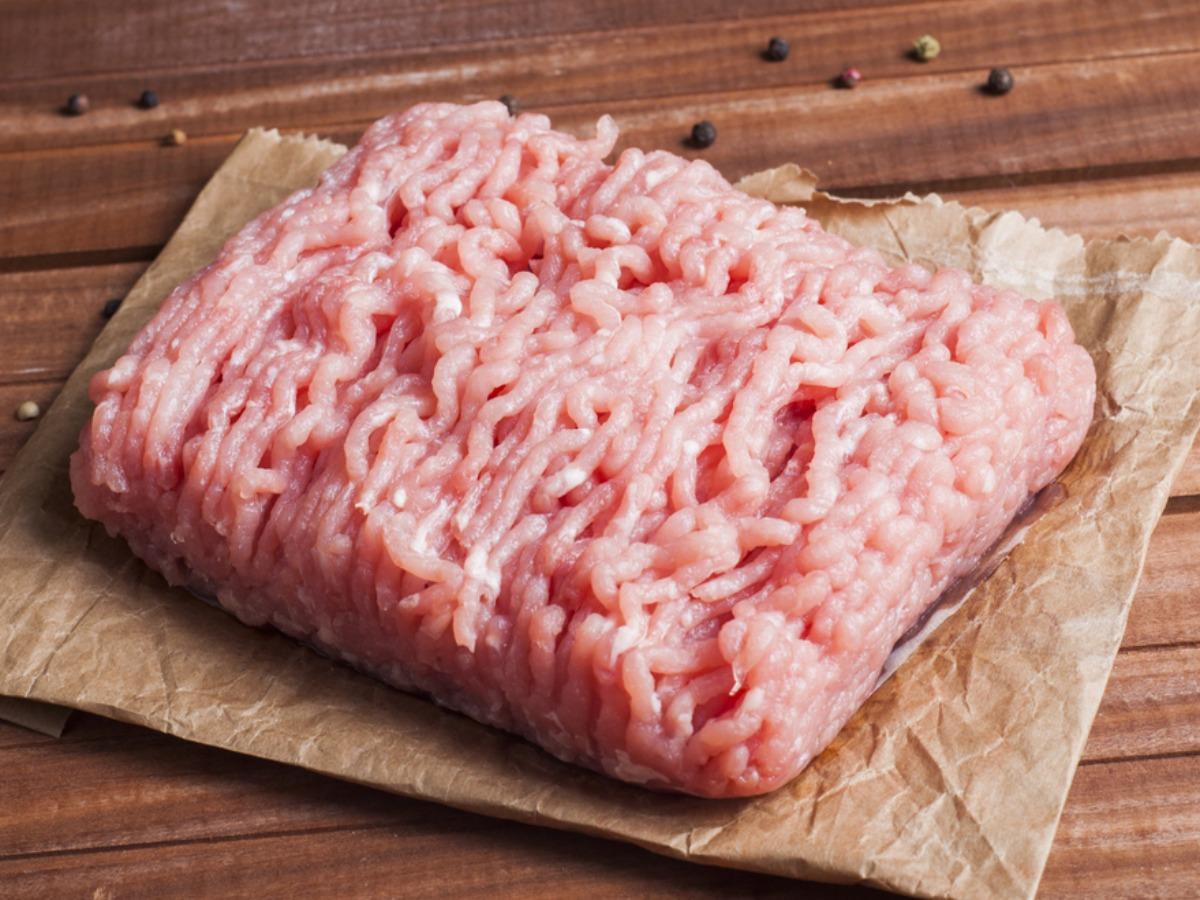

Ground Turkey Nutrition Facts - Eat This Much
/brine-for-chicken-and-turkey-996160-step-04-46933296fdff4d6fbecc22a24bea587d.jpg)
Should You Brine or Pre-Salt Your Turkey?

Nutrition: Let's talk turkey — and sodium | Duluth News Tribune

Oscar Mayer Turkey Bacon ‑ Shop Bacon at H‑E‑B

Lean Ground Turkey | JENNIE-O® Product

Turkey Brining Recipes and Tips | Epicurious.com | Epicurious.com
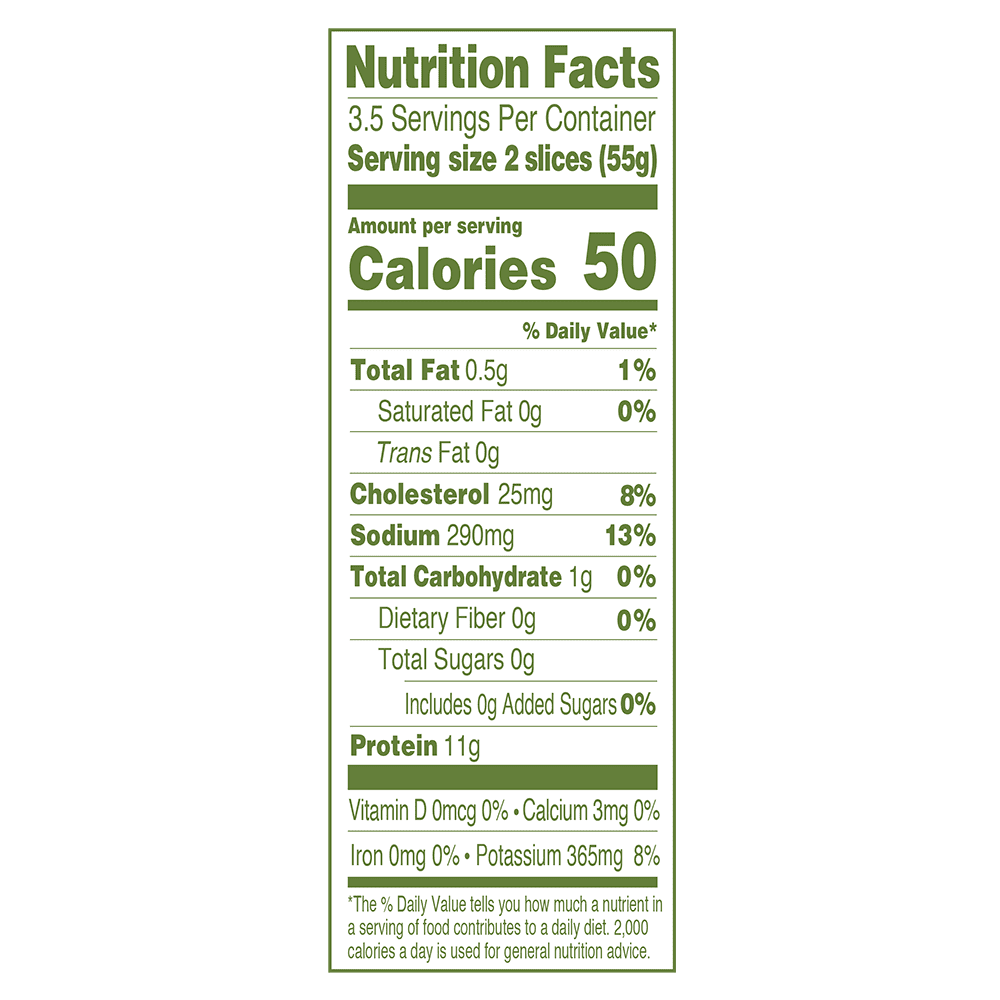
Products - Deli Meat - Natural Smoked Turkey Breast - Applegate

Grilled Roasted Salt & Pepper Turkey | Foodland
Products - Smithfield.com | Flavor hails from Smithfield.

Products - Deli Meat - Natural Smoked Turkey Breast - Applegate

How Does Brining Affect the Sodium Content of Meat?

Salt Reduced Bacon Style Turkey - Butterball

Taste-Off: The best deli turkey -- and the slimy, salty worst

Turkey Brine 101 (The BEST Wet and Dry Brines) | foodiecrush.com

Turkey Bacon: How Healthy Is It Really? – Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic
Sodium in turkey, per 100g - Diet and Fitness Today

Products - Bacon - Natural Turkey Bacon - Applegate

Turkey Bacon Nutrition Facts - Eat This Much
Posting Komentar untuk "how much sodium is in turkey"